Anti-Biofilm Wound Dressing Market (By Mode of Mechanism: Physical, Chemical, and Biological; By Application: Chronic Wounds, and Acute Wounds) - Global Industry Analysis, Market Size, Opportunities, and Forecast 2021 - 2028
Published :
Report ID:
Pages :
Format :
Anti-Biofilm Wound Dressing Market (By Mode of Mechanism: Physical, Chemical, and Biological; By Application: Chronic Wounds, and Acute Wounds) - Global Industry Analysis, Market Size, Opportunities, and Forecast 2021 - 2028
Report Coverage
- Industry Dynamics
- Market Size and Forecast Data
- Segment Analysis
- Competitive Landscape
- Regional Analysis with a Niche Focus on Country-Level Data
- High Level Analysis - Porter's, PESTEL, Value Chain, etc.
- Company Profiles of Key Players
- Option to Customize the Report As Per Your Specific Need
Request Sample Report
Introduction
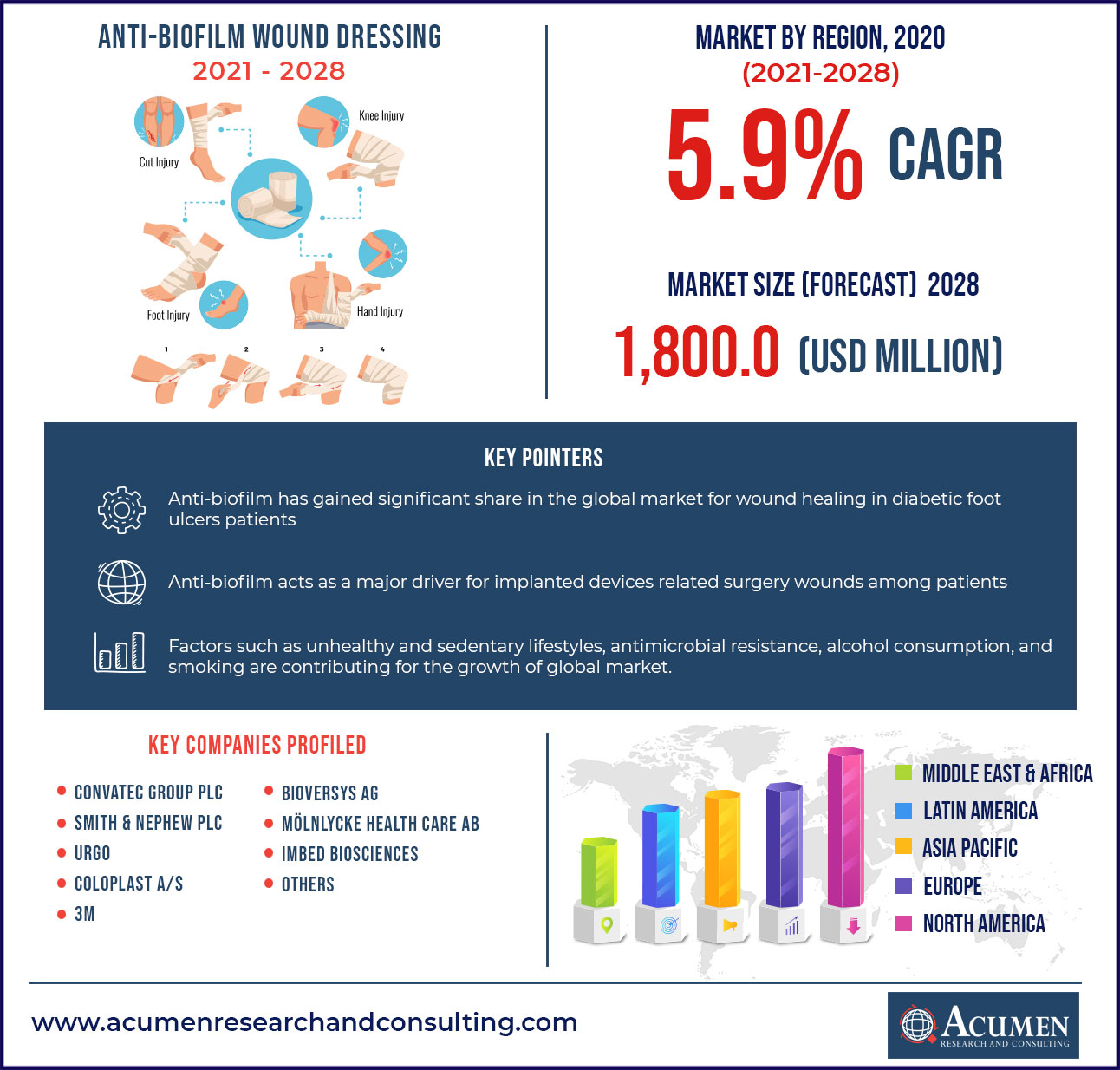
The global anti-biofilm wound dressing market is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 9.5% from 2021 to 2028 and is expected to reach a market value of around US$ 1,800 Mn by 2028.
Chronic wounds caused by diabetic ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous leg ulcers, as well as an ageing and obese population, are becoming increasingly important medical concerns in the developed world. Proper identification of bacterial biofilm contamination is a major contributor to non-healing wounds, necessitating biofilm-targeted treatments for chronic wounds. Novel, non-invasive physical debridement methods, chemical agent strategies, and biological agent strategies are among the emerging anti-biofilm strategies.
Market Dynamics
Anti-biofilm has gained significant share in the global market for wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers patients
According to Diabetes UK statistics from 2016, there is an occurrence of 59,000 active foot ulcers cases in England with along with 135 foot amputations diagnosis performed each week. With such a widespread problem, wound care must be both clinically effective and cost effective in order to help chronic wounds involving diabetic foot ulcers heal before they cause irreversible damage. Diabetic foot infections are a major problem worldwide, according to a report published in the Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal. For the record, diabetes affects over 62 million people in India. Foot ulcers are the most common problem associated with diabetes, and if left untreated, they can lead to limb amputation. They provide protection against host defenses due to their anti-biofilm properties. Today, biofilm polymers account for 75% of drug resistance bacteria, and this has a positive impact on the overall growth of the anti-biofilm wound dressing market.
COVID-19 impact on the global anti-biofilm wound dressing market
According to the American Chemical Society (ACS) report, the world has faced pandemic situations several times in the past, and due to the emergence of new pathogens, there has always been a need for new antimicrobial therapies. The increased demand for antimicrobial materials, particularly in the healthcare sector, has increased the potential market. Antibacterial and antiviral materials or surfaces have the potential to control healthcare-associated infections, thereby limiting the spread of pandemics such as COVID-19. Apart from that, metals such as silver and copper chemicals have shown promising antimicrobial properties when it comes to anti-biofilm wound dressing. On the other hand, it would be fantastic to introduce technology that focus on a machine-learning model trained on data from the literature to rapidly screen and check chemical and biological toxicity profiles in clinical trials for safe anti-biofilm wound dressing among patient group..during
Report coverage
| Market | Anti-Biofilm Wound Dressing Market |
| Analysis Period | 2017 - 2028 |
| Base Year | 2020 |
| Forecast Data | 2021 - 2028 |
| Segments Covered | By Mode of Mechanism, By Application and By Geography |
| Regional Scope | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
ConvaTec Group plc, Smith & Nephew PLC, URGO, Coloplast A/S, 3M, BioVersys AG, Mölnlycke Health Care AB, Imbed Biosciences and among others |
| Report Coverage |
Market Trends, Drivers, Restraints, Competitive Analysis, Player Profiling, Regulation Analysis |
| Customization Scope | 10 hrs of free customization and expert consultation |
Anti-biofilm acts as a major driver for implanted devices related surgery wounds among patients
Implanted devices are widely used in orthopaedic and trauma surgery to restore function and aid in the healing of broken bones, according to a Frontiers Media S.A. report. These interventions result in more rapid and accurate restoration of function, which improves the quality of life for affected patients. Nonetheless, orthopedic device-related infection (ODRI) poses a significant risk to the success of these surgical interventions. The incidence of ODRI ranges from 1 to 2% in cases of elective joint replacement to 30% in complex open fractures where the skin's protective barrier is breached. The implant's surface, in fact, serves as a substrate for bacterial attachment and the formation of biofilms that are much more resistant to antibiotics. The bacteria in the biofilm produce an extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) that acts as a matrix, preventing antimicrobials and host immune cells from penetrating the biofilm. As a result, novel biofilm and dispersal strategies are gaining traction, as their integration with conventional antimicrobial therapies reduces the risk of toxicity and resistance development. Such factors contribute to the overall growth of the global anti-biofilm wound dressing market.
Market Segmentation
The global anti-biofilm wound dressing market is segmented based on mode of mechanism and application. Mode of mechanism is segmented into physical, chemical, and biological. Physical segment is further segregated into manual debridement, pulse electrical field, and ultrasound debridement. Further, chemical segment is further split into Ionic silver, iodine, and Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). Biological segment is further segmented into Dispersin B, Lactoferrin, and Bacteriophage. Further, application is bifurcated into chronic wounds and acute wounds.
The chemical segment dominates the overall anti-biofilm wound dressing market in terms of mode of mechanism. Biofilm is formed by a variety of processes that are potentially reversible in the early stages of microbial colonization. As a result, chemicals become increasingly important as biofilm formation progresses and disruption and eradication become more difficult. Furthermore, in-vitro studies on chemicals have revealed that specific chemicals such as ionic silver, iodine, and EDTA, anti-biofilm play a critical role in wound healing inhibition activities among people. Such factors have positive influence for the segmental growth ultimately contributing for the overall market growth of anti-biofilm wound dressing.
According to application, the acute wounds segment accounts for the lion's share of the anti-biofilm market. Infection caused by orthopedic devices is still a serious problem that must be addressed. Orthopedic device-related infections (ODRI) place a significant burden on patients and healthcare systems due to the need for surgical revisions, prolonged antibiotic therapy, functional loss, and in some cases, salvage procedures involving amputation of the affected limb or establishment of a continuous fistula. As a result, anti-biofilm should be regarded as a critical target in the fight against ODRI. Surface modification, for example, by covalent attachment of anti-biofilm specific compounds, has shown promising results in ODRI prevention by inhibiting bacterial colonisation while allowing tissue integration. Such factors have a positive impact on segmental growth, which in turn contributes to market growth.
Regional Landscape
North America holds the dominating share for anti-biofilm wound dressing market
North America has the largest share of the anti-biofilm wound dressing market and is expected to maintain this trend throughout the forecast period. The presence of prominent players in this region is one of the key factors attributed to the significant regional revenue share.
Competitive Landscape
The prominent players of the global anti-film wound dressing market involve ConvaTec Group plc, Smith & Nephew PLC, URGO, Coloplast A/S, 3M, BioVersys AG, Mölnlycke Health Care AB, Imbed Biosciences and among others
Market Segmentation
Market by Mode of Mechanism
- Physical
- Manual Debridement
- Pulse Electrical Field
- Ultrasound Debridement
- Chemical
- Ionic Silver
- Iodine
- EDTA
- Others
- Biological
- Dispersin B
- Lactoferrin
- Bacteriophage
- Others
Market by Application
- Chronic Wounds
- Acute Wounds
Market By Geography
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- U.K.
- Germany
- France
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Australia
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
How much will be the projected value of the global Anti-Biofilm wound dressing market in 2028?
The market value of around US$ 1,800 Mn by 2028 and CAGR of around 9.5% from 2021 to 2028
Which are the prominent competitors operating in the market?
ConvaTec Group plc, Smith & Nephew PLC, URGO, Coloplast A/S, 3M, BioVersys AG M�lnlycke Health Care AB, Imbed Biosciences and among others
Which region held the highest market share ?
North America is anticipated to grab the highest market share in the regional market and Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest growing market in the forthcoming years


